Food
Cashew | Fruit, Types, Health Benefits
Cashews are a popular type of nut that is loved by many for their unique shape, creamy texture, and delicious taste. These kidney-shaped nuts are native to Brazil but are now grown in tropical regions around the world. Cashews are not only a tasty snack but also offer a range of health benefits.
Species or Types of Cashew
The cashew tree, scientifically known as Anacardium occidentale, belongs to the Anacardiaceae family and is native to Brazil. It is cultivated for its cashew nuts and cashew apples. There are different species and varieties of cashew trees, but the most commonly cultivated and commercially important species is Anacardium occidentale. This species is widely grown in tropical regions around the world for its edible nuts and fruits.
While Anacardium occidentale is the primary species cultivated for cashew nuts, there are other related species within the Anacardium genus. Some of these species include:
- Anacardium giganteum: This species is native to South America and is known for its large size compared to Anacardium occidentale. It produces similar edible nuts and fruits.
- Anacardium humile: Also native to South America, this species is commonly referred to as the Monkey Nut tree. It produces small, kidney-shaped nuts that are also edible.
- Anacardium excelsum: This species is found in Central and South America and is known for its tall stature and large leaves. It produces edible nuts similar to Anacardium occidentale.
While Anacardium occidentale remains the most widely cultivated species for cashew nuts, these related species within the Anacardium genus also contribute to the diversity of cashew trees in different regions. Each species may have unique characteristics in terms of nut size, flavor, or growth habits, adding to the richness of the cashew tree family.
Uses of Cashew
Cashews have a wide range of culinary and non-culinary uses due to their unique taste, texture, and nutritional properties. Here are some common uses of cashews:
- Snacking: Cashews are often enjoyed as a delicious and nutritious snack on their own, either raw or roasted and salted. They can also be included in trail mixes or nut mixes for a satisfying on-the-go snack.
- Cooking and Baking: Cashews are a versatile ingredient in both savory and sweet dishes. They can be used to add creaminess to vegan sauces, soups, and dips. Cashew butter is a popular alternative to peanut butter and can be spread on toast or used in baking recipes.
- Dairy Alternatives: Cashews can be used to make dairy-free alternatives such as cashew milk, cashew cream, and cashew cheese. These products are suitable for individuals with lactose intolerance or those following a vegan diet.
- Nutritional Boost: Cashews can be ground into a flour or meal and used in gluten-free baking recipes. They can also be sprinkled on salads, yogurt, or oatmeal for added crunch and nutrition.
- Garnishing: Cashews can be chopped or crushed and used as a topping for various dishes such as salads, stir-fries, curries, and desserts. They add a crunchy texture and nutty flavor to the dish.
- Nutritional Supplements: Cashew nuts can be processed into cashew butter or cashew oil, which can be used as a source of healthy fats and nutrients in smoothies, dressings, or as a cooking oil.
- Traditional Medicine: In some cultures, cashews are believed to have medicinal properties and are used in traditional herbal remedies for ailments such as stomach issues, skin conditions, and even snake bites. However, it’s essential to consult a healthcare professional before using cashews for medicinal purposes.
- Industrial Uses: Cashew nut shell liquid (CNSL), a byproduct of cashew processing, is used in various industrial applications such as in the production of paints, varnishes, and insecticides.
Health Benefits
- Heart Health: The healthy fats found in cashews, such as oleic acid, have been linked to improved heart health by reducing bad cholesterol levels and lowering the risk of heart disease.
- Weight Management: Despite being calorie-dense, cashews can aid in weight management due to their high fiber and protein content. These nutrients help keep you feeling full and satisfied, reducing the likelihood of overeating.
- Bone Health: Cashews are a good source of minerals like magnesium, phosphorus, and copper, which are essential for maintaining strong and healthy bones.
- Antioxidant Properties: Cashews contain antioxidants like vitamin E and selenium, which help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals and oxidative stress.
Disadvantages of Cashew
While cashews are nutritious and delicious, there are a few potential disadvantages associated with their consumption that individuals should be aware of. Here are some common disadvantages of cashews:
- Allergies: Cashew nuts are one of the tree nuts that people commonly have allergies to. Cashew allergies can range from mild reactions like itching and hives to severe symptoms such as swelling, difficulty breathing, and anaphylaxis. Individuals with tree nut allergies should avoid cashews and products containing cashew ingredients.
- Oxalate Content: Cashews are relatively high in oxalates, which are compounds that can bind to calcium in the body and potentially contribute to the formation of kidney stones in susceptible individuals. People prone to kidney stones may need to moderate their intake of high-oxalate foods like cashews.
- Calorie Density: Cashews are calorie-dense nuts due to their high fat content, which can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess. Portion control is essential when enjoying cashews as a snack or ingredient in dishes to avoid consuming an excessive number of calories.
- Fungal Contamination: Cashew nuts grow in a shell attached to a “cashew apple,” and improper processing can lead to fungal contamination on the nuts. Aflatoxins, produced by certain molds, can develop on cashews if they are not stored or processed correctly. Aflatoxins are toxic compounds that can be harmful if ingested in large amounts. Proper storage and processing methods are crucial to prevent fungal contamination.
Food
Ryze Mushroom Coffee Ingredient, Review, Buy or Not?

Ryze mushroom coffee is an organic, gluten-free coffee that provides a lot of health benefits. It’s not every day that you get to find organic products on the market to buy, and so we often encourage businesses that produce their products organically.
What is Ryze mushroom coffee?
Ryze mushroom coffee is powdered extract of medicinal mushrooms like Cordyceps, Lion’s Mane, Reishi, King Trumpet, Shiitake, and Turkey Tail. which are mixed with coffee in a ratio of 1:1 to give it a perfect blend of coffee and mushroom flavor. The reason why this kind of combination is important is the fact that mushrooms have historically proven to be nutritious with numerous health benefits. In World War II, people from Finland made their coffee from mushrooms and a little bit of coffee beans due to the scarcity of the commodity at the time. It was around that time that it was invented, and still in 2025, the legacy still lives on. Mushroom coffees are now growing in popularity due to the discovery people have made into it, realizing its nutritional values. Ryze mushroom coffee is produced by Ryze Superfoods in the United States. The company disclosed that all of the ingredients used to make the mushroom coffee are organic, and it sources these ingredients from California and Nevada.
Ingredients
1. Cordyceps
- Energy Boost: Cordyceps is known to help increase energy and stamina by improving the body’s production of ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is crucial for energy.
- Antioxidant Properties: It contains antioxidants that help fight off free radicals, reducing oxidative stress.
- Immune Support: It may enhance the immune system by stimulating the production of certain immune cells.
- Improved Exercise Performance: Some studies show it may improve oxygen utilization during exercise, enhancing physical endurance.
2. Lion’s Mane
- Brain Health: Lion’s Mane is known for supporting cognitive function, improving memory, and possibly aiding in neurogenesis (growth of new brain cells).
- Mental Clarity and Focus: It can help reduce brain fog and improve focus and concentration.
- Mood Enhancement: It may have mood-boosting effects, helping to reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression by enhancing neurochemical balance.
- Nerve Regeneration: Studies suggest Lion’s Mane could promote the repair of nerve damage, potentially helping with neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s.
3. Reishi
- Immune System Support: Reishi is known for its ability to strengthen the immune system. It has adaptogenic properties that help the body respond to stress.
- Heart Health: It may help reduce blood pressure and cholesterol, contributing to better cardiovascular health.
- Anti-inflammatory Effects: Reishi has anti-inflammatory properties that may assist in reducing inflammation in the body.
- Promotes Relaxation: It has calming effects that can help reduce stress, anxiety, and promote better sleep.
4. Shiitake
- Rich in Nutrients: Shiitake mushrooms are a great source of B-vitamins, such as B2, B5, and B6, as well as essential minerals like copper and selenium.
- Immune System Boost: Shiitake contains compounds that support immune health, such as lentinans, which enhance the body’s ability to fight infections.
- Heart Health: It can lower cholesterol levels and may help reduce the risk of heart disease due to its beta-glucans and sterols.
- Anti-cancer Properties: Shiitake has been studied for its potential to inhibit cancer cell growth, particularly through its lentinans and other bioactive compounds.
5. Turkey Tail
- Immune Support: Turkey Tail is renowned for its ability to boost immune function. It contains polysaccharides that activate immune cells, helping fight infections.
- Gut Health: It supports gut health by promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria, which aids digestion and nutrient absorption.
- Anti-inflammatory: It has anti-inflammatory effects that may reduce the risk of chronic diseases linked to inflammation.
- Potential Anti-cancer Effects: Some studies suggest it may help support cancer treatments by enhancing immune function.
6. King Trumpet
- Immune System Enhancement: King Trumpet mushrooms contain beta-glucans that can enhance immune function and help combat infections.
- Antioxidant Properties: They have antioxidant compounds that help protect cells from damage and slow down aging processes.
- Liver Health: These mushrooms may assist in detoxification processes by promoting liver health.
- Support for Heart Health: They contain compounds that can help reduce cholesterol and support overall cardiovascular health.
7. Organic Arabic Coffee
- Rich in Antioxidants: Arabic coffee is loaded with antioxidants that can help reduce oxidative stress and protect against chronic diseases.
- Improved Cognitive Function: The caffeine in Arabic coffee enhances alertness, focus, and cognitive performance.
- Boosts Metabolism: Caffeine can increase metabolism, helping with weight management and fat burning.
- Mood and Energy Boost: The caffeine also stimulates the production of feel-good hormones like dopamine and serotonin, which can help improve mood and reduce fatigue.
8. Organic MCT Oil & Coconut Oil Milk
- Quick Source of Energy: MCT oil provides fast-acting energy because it is easily absorbed and converted into ketones, which can fuel the brain and body.
- Support for Ketosis: It’s ideal for those on a ketogenic diet as it helps the body maintain ketosis, promoting fat burning for energy.
- Cognitive Benefits: MCT oil has been shown to support brain function and may help in reducing cognitive decline.
- Gut Health: Coconut oil contains lauric acid, which has antimicrobial properties that may support gut health and fight infections.
- Weight Loss: MCT oil can help control appetite, making it easier to manage weight by reducing hunger.
These ingredients combine to give the body what it needs the most like A boost in metabolism, A better sleep, Healthy digestion, Immune support, Energy and many others.
What are the nutritional benefits?
Ryze Mushroom Coffee is 100% vegan and contains several nutritional benefits, including what I have listed in the table below:
| Calories | 15 |
| Total fat | 1g |
| Saturated fat | 1g |
| Trans fat | 0g |
| sodium | 0mg |
| Total Carbohydrate | Less than 1g |
| Protein | 0g |
How to prepare
- Scoop one to two tablespoons of Ryze mushroom coffee.
- Pour the powder into 9-11 oz of hot water and stir.
- You can add milk to it to improve the taste and nutrients.
Design
Packaging is important in describing what can be found in it and whether it’s a premium or just a low-budget product. Big brands often ensure to get the best packaging possible, and in the case of Ryze mushroom coffee, it’s sealed in a 6.35 oz. sachet colored with coffee color to enable consumers to feel the vibe. The downside of Ryze’s package is that it does not portray a picture of mushrooms and coffee, but rather a picture of a flower drawn on it.
Price and where to buy
Ryze mushroom coffee is quite popular on the market; therefore, locating it on various supermarket shelves shouldn’t be a problem. Amazon, eBay, and Walmart also sell Ryze mushroom coffee. Below is a table that shows the price of Ryze mushroom coffee on each platform.
| Ryzesuperfoods.com | $27 |
| Amazon | $29 |
| eBay | $34 |
Ryze food products
Ryze produces a wonderful number of other organic products besides the mushroom coffee.
Mushroom Chicory
This is caffeine-free coffee, and it’s made up of chicory root and a 6-mushroom blend.
Nutritional Facts
| Calories (amount per serving) | 23 |
| Total Fat | 1g |
| Saturated fat | 1g |
| Sodium | 3mg |
| Carbohydrate | 2g |
| Dietary Fibre | 1g |
| Sugars | 0g |
| Protein | 0g |
| Potassium | 20mg |
Mushroom Chai
RYZE Chai is packed with 6 adaptogenic mushrooms and warming Ayurvedic spices.
Mushroom Hot Cocoa
100% organic cacao with no added sugar.
Superfood Creamer
100% organic superfoods, hydrating coconut water, and one billion CFU of probiotics
Nutritional Facts
| Calories (amount per serving) | 35 |
| Total Fat | 1.5g |
| Saturated fat | 1.5g |
| Trans Fat | 0g |
| Cholesterol | 0mg |
| Sodium | 0mg |
| Carbohydrate | 5g |
| Dietary fibre | 0g |
| Sugar | 3g |
| Protein | 0g |
| Calcium | 10mg |
| Iron | 0.6mg |
| Potassium | 120mg |
Mushroom Matcha
The product is made of six mushroom blends, blue spirulina, coconut milk powder, organic MCT oil powder, and organic Himalayan pink salt.
Nutritional Facts
| Calories (amount per serving) | 25 |
| Total Fat | 2.5g |
| Saturated fat | 2.5g |
| Trans Fat | 0g |
| Sodium | 0mg |
| Carbohydrate | 1g |
| Protein | 0g |
Mushroom Coffee VS Traditional Coffee
The mushroom coffee and the traditional coffee, which is made out of only coffee beans, have their individual advantages. Before the invention of mushroom coffee, the world only knew of the traditional coffees. The mushroom coffee originated in Finland during World War II and became popular when people noticed the enormous health benefits it possesses. The mushroom coffees are made out of a blend of coffee beans and an extract of medicinal mushrooms like Cordyceps, Lion’s Mane, Reishi, Shiitake, Turkey Tail, King Trumpet, and others. This combination even gives some coffee taste resemblance but does not give a true taste like the traditional coffee, which is composed of about 90% to 100% coffee. If you seek my opinion, mushroom coffees are great for medicinal purposes, while traditional coffees are great for recreational use.
Frequently Asked Questions
Does Ryze mushroom coffee contain caffeine?
Yes, this product contains 48mg of caffeine, which is less than what you would find in a regular coffee.
Do these products contain any additives?
Additives are substances added to food or products to enhance their flavor, appearance, shelf life, or other properties. While many additives are generally regarded as safe by food safety authorities, their impact on human health can vary depending on the type, quantity, and frequency of consumption. However, Ryze mushroom coffee does not contain any additives at all.
Is this product organic?
Yes, one of the reasons why this product does not contain any additives is that they are organic.
Who is this product not good for?
This product is not recommended for people allergic to caffeine, pregnant or breastfeeding mothers.
Where can I buy this product?
If you want to buy this product from Ryzesuperfoods’ official website, it is possible but they only supply within the United States. If you live outside of the United States, like Canada, United Kingdom, Australia, Germany, Mexico etc. then you should probably consider making your order on Amazon and eBay from third party sellers who are ready to ship to your destination.
Food
Takis Ingredients and Honest Review

Takis are in the form of rolled tortilla chips, which were launched in Mexico but are now produced in many parts of the world. This amazing snack has been produced by Grupo Bimbo’s subsidiary Barcel since the year 2019.
What is Takis?
You probably see a lot of snacks around you everyday but only a few get well branded and noticed, just like Takis. Takis is a Mexican-flavored snack that has broken boundaries into other countries’ shelves with its sweet taste. As we already know, Mexico is also home to some of the world’s most delicious foods in different varieties, like the famous Tacos, Gorditas, Quesadillas and more. Currently, Takis is available in world markets like Brazil, Argentina, Canada, the United States, South Korea, Japan, the United Kingdom, the European Union, New Zealand, and Australia, with different varieties all produced by Barcel.
Takis Rolls Flavors
In order not to get consumers stuck with only one taste and flavor, Barcel has other lineups of Takis that deliver different tastes yet are very capable of giving your taste buds a satisfying treat. The first one we will look at is the Takis Rolls, which currently has over 11 flavors, and below is a list of them.
- Takis Intense Nacho Rolls
- Takis Chile Limón Rolls
- Takis Burkin Ranch Rolls
- Takis Nacho Xplossion Rolls
- Takis Dragon Sweet Chili Rolls
- Takis Crunchy Fajitas Rolls
- Takis Guacamole Rolls
- Takis Cobra Rolls
- Takis Nitro Rolls
This is a lime-flavored tortilla chips which is spicy and delicious. The nitro and fuego flavor gives the chips a reddish color. That is why you see your Nitro Takis Red.
- Takis Fuego Rolls
This Tortilla Chip is hailed by many consumers of its great taste and rightly so, it’s one of the brand’s popular chips. And you can find different sizes ranging from 1 oz, 1.23 oz, 3.25 oz and 9.9 oz.
Ingredients
- Corn Flour
- Vegetable Fat(Palm)
- Prepared Chilli
- Lime-Flavored Condiment
- Acidity Regulators(Citric Acid, Sodium Carbonates, Sodium Acetates)
- Sugar
- Flavor Enhancers (Monosodium Glutamate, Disodium 5*-Ribonucleotides, Yeast Extract, Powdered Onion)
- Colors (Paprika Extract, Carmine)
- Takis Blue Heat Rolls
From production, there are 14 Blue Heat Rolls in a box and each one weighs 9.9oz.
Ingredients
- Corn Flour (Processed with lime)
- Vegetable Oil
- Maltodextrin
- Citric acid
- Sugar,
- Potassium chloride
- Salt
- Monosodium glutamate
- Hydrolyzed soybean protein
- Natural and artificial flavors
- Hydrolyzed yeast
- Soybean oil
- Onion powder
- Blue 1 lake
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Chili pepper (chile)
- Disodium inosinate
- Disodium guanylate
- TBHQ (preservative)
Takis Waves Flavors
Lucky for potato lovers, this variety is primarily made of Potato with other ingredients to give it the best crunchy taste. Ideal for those who want a bit of sugar taste. The flavors for the wave are listed below;
- Takis Fuego Waves
- Takis Blue Heat Waves
- Takis Dragon Sweet Chili Waves
Takis Kettlez
The Kettlez variety has three strong flavors and they are below.
- Takis Fuego Kettlez
- Takis Habanero Fury Kettlez
- Takis Jalapeno Typhoon Kettlez.
Takis Chippz
This come variety has only one flavor which is the Takis Fuego Chippz.
Design
Any of the Takis flavors are rolled into stick forms. The chips, which are also a good snack, are produced in different flavors and are packed in sachet bags, which come in different colors for easy identification of flavors. These sachets are also designed in different sizes to best suit the budget of any consumer, and that is why there is Takis Mini. Takis bags come in colors like red, purple, and orange, with Takis boldly written on them.
Health Benefits of Takis
Many people have reservations about processed foods and spices; however, these processed foods can also provide some health benefits if consumed with caution. Below are some health benefits of ingredients used in making Takis.
Maltodextrin
Health Benefit: Maltodextrin is a carbohydrate derived from starch and is commonly used as a food additive. It provides a quick source of energy due to its rapid absorption by the body. It may also help in replenishing glycogen stores post-exercise, making it popular in energy drinks and supplements.
Citric Acid
Health Benefit: Citric acid, found in citrus fruits, has antioxidant properties and may help in improving digestion by stimulating the production of gastric juices. It also helps prevent kidney stone formation and supports the absorption of minerals like calcium.
Sugar
Health Benefit: Sugar, particularly in moderation, provides a quick source of energy to the body. It is important for brain function and provides fuel for cells, but excessive sugar intake can lead to health issues like obesity and diabetes.
Potassium Chloride
Health Benefit: Potassium chloride is a source of potassium, an essential mineral that helps regulate fluid balance, muscle contractions, and nerve signals. It is particularly important for heart health, helping to control blood pressure levels.
Salt
Health Benefit: Salt is vital for the body as it helps maintain fluid balance, nerve function, and muscle contractions. However, excessive salt intake can lead to high blood pressure and other health problems.
Monosodium Glutamate (MSG)
Health Benefit: MSG is commonly used as a flavor enhancer. Some studies suggest that MSG can enhance the flavor profile of food without adding extra salt, helping in reducing overall sodium intake. It is also thought to promote the sensation of umami, one of the five basic tastes.
Hydrolyzed Soybean Protein
Health Benefit: Hydrolyzed soybean protein is rich in amino acids and can be a good protein source, especially for vegetarians or those who are lactose intolerant. It may help with muscle repair and maintenance.
Hydrolyzed Soybean Protein
Health Benefit: Hydrolyzed soybean protein is rich in amino acids and can be a good protein source, especially for vegetarians or those who are lactose intolerant. It may help with muscle repair and maintenance.
Hydrolyzed Yeast
Health Benefit: Hydrolyzed yeast is a good source of B vitamins, particularly B12, which is important for energy production, brain health, and nerve function. It is also a good source of glutamic acid, an amino acid that plays a role in the nervous system.
Soybean Oil
Health Benefit: Soybean oil contains polyunsaturated fats, which are beneficial for heart health. It also contains omega-3 fatty acids, which help in reducing inflammation and promoting brain health. However, excessive consumption of processed oils should be avoided.
Onion Powder
Health Benefit: Onion powder has antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. It may support heart health, reduce the risk of certain cancers, and improve digestion due to its rich content of vitamins and minerals.
Blue 1 Lake
Health Benefit: Blue 1 is a synthetic dye used to color food and beverages. While there are no significant health benefits, it is approved for use in food and cosmetics. However, some individuals may have sensitivities to artificial colorings, which could cause allergic reactions.
Sodium Bicarbonate (Baking Soda)
Health Benefit: Sodium bicarbonate is commonly used to help relieve heartburn and indigestion. It may also help with kidney function, balance the body’s pH, and neutralize acids. It is often used as an antacid.
Chili Pepper (Chile)
Health Benefit: Chili peppers are rich in capsaicin, which has antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and metabolism-boosting properties. They may help in weight management by promoting fat burning, improving digestion, and alleviating pain.
Disodium Inosinate
Health Benefit: Disodium inosinate is often used as a flavor enhancer in combination with MSG. It can enhance the umami taste and may help in reducing the need for excess salt in foods. It is considered safe in the amounts used in food.
Disodium Guanylate
Health Benefit: Like disodium inosinate, disodium guanylate is a flavor enhancer often used in conjunction with MSG. It can contribute to the umami taste and can help in improving the taste profile of processed foods.
TBHQ (Tert-Butylhydroquinone)
Health Benefit: TBHQ is a synthetic antioxidant used to preserve food and prevent oxidation, which helps in extending shelf life. It may have some protective effects against oxidative stress but should be consumed in moderation as high intake could lead to potential health risks.
Price and where to buy
Takis Snacks are available in many countries therefore can be found in malls, supermarkets, online platforms and even small grocery stores. If you find yourself in the United States, United Kingdom, Canada and places where Amazon and eBay works. Different varieties of Takis are listed for sale on these platforms. Takis products are priced according to size and flavor and so I have listed some of the flavors and their prices below:
| Takis Fuego Mini 25 pc / 1.23 oz Bite Size Multipack | $14.24 |
| Takis Blue Heat Mini 25 pc / 1.23 oz Bite Size Multipack | $14.68 |
| Takis Intense Nacho 40 pc / 1 oz Multipack | $23.29 |
| Barcel Takis Nitro Habanero & Lime Tortilla Chips, 9.9 Oz | $23.29 |
| Barcel Takis Nitro Habanero & Lime Tortilla Chips, 9.9 Oz | $29.86 |
| Takis Guacamole Rolled Tortilla Chips | $8.65 |
Food
Cheetos Snacks Ingredients and Honest Review
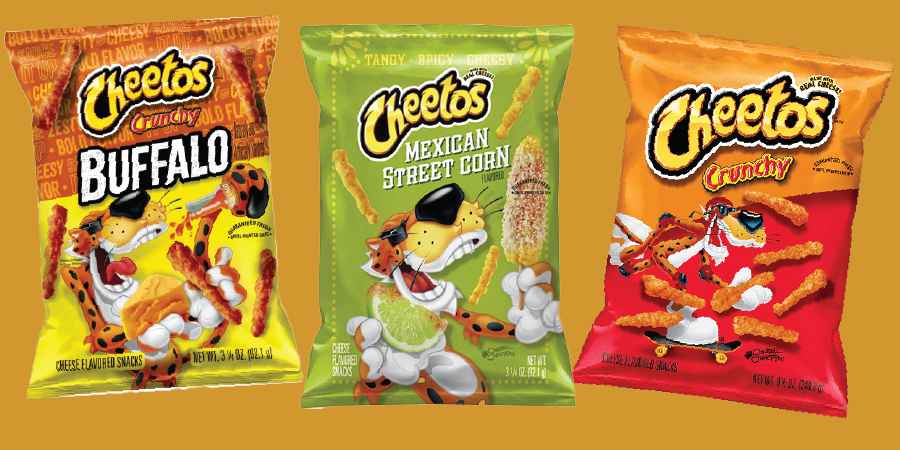

Cheetos are delicious snacks produced by the PepsiCo group in the United States. Good snacks are not only for satisfaction but are also nutritious for the body. Now the question is, which snack is best for consumption? Let’s examine the ingredients that make Cheetos unique. This explains why Cheetos are considered one of the best snacks to look out for.
About Cheetos
Cheetos were launched in 1948 by Charles Elmer Doolin, and it was branded as Cheetos until 1998, when it was changed to Crunchy Corn Cheese Puff. Frito-Lay is the current producer of Cheetos, and they are mainly distributed in the United States. In 2010, Cheetos was seen as one of the top cheese puffs in the United States. Beyond the United States, Cheetos are also on the shelves of supermarkets in other parts of the world. Again, it is estimated that Cheetos have a worldwide retail sales of $4 billion annually. Would you find it surprising to know that Cheetos is sold in over 36 countries? Well, yes. The original Crunchy Cheetos have been expanded to include other varieties, and these are sold in over 36 countries.
Types of Cheetos
After being in existence for over 77 years, the company has really expanded its branches and the variety of Cheetos they produce. The company currently produces a total of 21 Cheetos varieties. But do all of them have the same nutritional benefits? Let’s have a look at some of the Cheetos varieties, their ingredients, and their nutritional facts.
Cheetos Crunchy
The Crunchy Cheetos was the first or original variety, and it has now been produced in different varieties.
Cheetos Crunchy Cheese Flavored Snacks
Ingredients
- Corn Meal
- Ferrous Sulfate
- Niacin
- Thiamin Mononitrate
- Riboflavin
- Folic Acid
- Corn Oil
- Canola Oil
- Sunflower Oil
- Whey
- Milk
- Cheese Cultures
- Salt
- Enzymes
- Salt
- Corn Maltodextrin
- Natural Protein Concentrate
- Monosodium Glutamate
- Lactic Acid
- Citric Acid
- Artificial Color (Yellow 6)
Nutritional Benefits
The Crunchy Cheese flavor weighs 28g and it has 21 pieces in the sachet. In total you have 160 calories, 1.5g saturated fat, 200mg sodium and 1g sugar.
| Nutrient | Quantity | Percentage |
| Total Fat | 10g | 13% |
| Saturated Fat | 1.5g | 8% |
| Trans Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 200mg | 9% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 15g | 6% |
| Dietary Fiber | <1g | 3% |
| Total Sugars | 1g | |
| Protein | 2g | |
| Vitamin D | 0 mcg | 0% |
| Calcium | 10mg | 0% |
| Iron | 0.6mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 60mg |
Cheetos Crunchy Flamin Hot Cheese Flavored Snacks
Ingredients
Enriched Cord Meal
- Corn Meal
- Ferrous Sulfate
- Niacin
- Thiamin Mononitrate
- Riboflavin
- Folic Acid
Vegetable Oil
- Corn Oil
- Canola Oil
- Sunflower Oil
- Salt
- Maltodextrin
- Yeast Extract
- Monosodium Glutamate
- Potassium Salt
- Citric Acid
- Sugar
Artificial Color
- Red 40 Lake
- Yellow 6 Lake
- Yellow 6
- Yellow 5
Cheddar Cheese
- Milk Cheese Cultures
Salt
Enzymes
Onion Powder
Whey
Whey Protein Concentrate
Garlic Powder
Natural Flavors
Buttermilk
Sodium Diacetate
Disodium Inosinate
Disodium Guanylate
Nutritional Benefits
The Crunchy Flamin Cheese flavor weighs 28g and it has 21 pieces in the sachet. In total you have 160 calories, 1.5g saturated fat, 210mg sodium and 0g sugar.
| Nutrient | Quantity | Percentage |
| Total Fat | 11g | 14% |
| Saturated Fat | 1.5g | 8% |
| Trans Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 210mg | 9% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 15g | 5% |
| Dietary Fiber | <1g | 3% |
| Total Sugars | 0g | |
| Protein | 1g | |
| Vitamin D | 0 mcg | 0% |
| Calcium | 10mg | 0% |
| Iron | 0.6mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 90mg |
Cheetos Crunchy Flamin Hot Limón Cheese Flavored Snacks
Ingredients
Enriched Corn Meal
- Corn Meal Ferrous Sulfate
- Niacin
- Thiamin Mononitrate
- Riboflavin
- Folic Acid
Vegetable Oil
- Corn Oil
- Canola Oil
- Sunflower
- Salt
- Yeast Extract
- Monosodium Glutamate
- Potassium Salt
- Citric Acid
- Maltodextrin (Made From Corn)
Artificial Color
- Red 40 lake
- Yellow 6 Lake
- Yellow 6
- Yellow 5
Corn Syrup Solids
- Hydrolyzed Corn Protein
Cheddar Cheese
- Milk
- Cheese Cultures
- Salt
- Enzymes
Onion Powder
Sugar
Whey
Lime Juice
Whey Protein Concentrate
Garlic Powder
Natural Flovors
Buttermilk
Sodium Diacetate
Disodium Inosinate
Disodium Guanylate
Nutritional Benefits
The Crunchy Flamin Hot Limon Cheese flavor weighs 28g and it has 21 pieces in the sachet. In total you have 160 calories, 1.5g saturated fat, 200mg sodium and 0g sugar.
| Nutrient | Quantity | Percentage |
| Total Fat | 11g | 14% |
| Saturated Fat | 1.5g | 7% |
| Trans Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 200mg | 9% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 15g | 5% |
| Dietary Fiber | <1g | 3% |
| Total Sugars | 0g | |
| Protein | 1g | |
| Vitamin D | 0 mcg | 0% |
| Calcium | 10mg | 0% |
| Iron | 0.6mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 100mg | 2% |
Cheetos Crunchy XXTRA Flamin Hot Cheese Flavored Snacks
Ingredients
Enriched Corn Meal
- Cord Meal
- Ferrous Sulfate
- Niacin
- Thiamin Mononitrate
- Riboflavin
- Folic Acid
Vegetable Oil
- Corn Oil
- Canola Oil
- Sunflower Oil
Salt
Maltodextrin (Made From Corn)
Yeast Extract
Sugar
Monosodium Glutamate
Citric Acid
Artificial Color
- Red 40 Lake
- Yellow 6 Lake
- Yellow 6
- Yellow 5
Hydrolyzed Corn Protein
Cheddar Cheese
- Milk
- Cheese Cultures
- Enzymes
- Potassium Salt
Onion Powder
Whey
Garlic Powder
Natural Flavors
Whey Protein Concentrate
Buttermilk
Sodium Diacetate
Nutritional Benefits
| Nutrient | Quantity | Percentage |
| Total Fat | 10g | 13% |
| Saturated Fat | 1.5g | 7% |
| Trans Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 210mg | 9% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 15g | 6% |
| Dietary Fiber | <1g | 3% |
| Total Sugars | 1g | |
| Protein | 2g | |
| Vitamin D | 0 mcg | 0% |
| Calcium | 10mg | 0% |
| Iron | 0.7mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 80mg | 0% |
Cheetos Crunchy Cheddar Jalapeño Cheese Flavored Snacks
Ingredients
Enriched Corn Meal
- Corn Meal
- Ferrous Sulfate
- Niacin
- Thiamin Mononitrate
- Riboflavin
Vegetable Oil
- Corn Oil
- Canola Oil
- Sunflower Oil
Salt
Whey
Maltodextrin
Cheddar Cheese
- Milk
- Cheese Cultures
- Enzymes
- Potassium Salt
Buttermilk
Monosodium Glutamate
Romano Cheese
- Cow’s Milk
Onion Powder
Corn Starch
Natural and Artificial Flavors
Spices
Lactose
Jalapeno Peppers
Garlic Powder
Whey Protein Concentrate
Artificial Color
- Yellow 6
- Yellow 5
- Blue 1
- Red 40
Sodium Caseinate
Skim Milk
Citric Acid
Malic Acid
Lactic Acid
Disodium Inosinate
Disodium Guanylate
Nutritional Benefits
The Crunchy Cheddar Jalapeno Cheese flavor weighs 28g and it has 21 pieces in the sachet. In total you have 160 calories, 1.5g saturated fat, 200mg sodium and less than 1g sugar.
| Nutrient | Quantity | Percentage |
| Total Fat | 10g | 13% |
| Saturated Fat | 1.5g | 7% |
| Trans Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 200mg | 9% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 15g | 6% |
| Dietary Fiber | <1g | 3% |
| Total Sugars | <1g | |
| Protein | 2g | |
| Vitamin D | 0 mcg | 0% |
| Calcium | 10mg | 0% |
| Iron | 0.6mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 130mg | 2% |
Cheetos Flamin Hot Tangy Chili Fusion Flavored Snacks
Ingredients
Enriched Corn Meal
- Corn Meal
- Ferrous Sulfate
- Niacin
- Thiamin Mononitrate
- Riboflavin
- Folic Acid
Vegetable Oil
- Corn Oil
- Canola Oil
- Sunflowers Oil
Natural and Artificial Flavors
Maltodextrin (Made From Corn)
Salt
Citric Acid
Sugar
Monosodium Glutamate
Dextrose
Spices
- Chili Peppers
- Red Peppers
- Garlic Powder
- Onion Powder
- Red Bell Peppers
Artificial Color
- Red 40 Lake
- Yellow 5 Lake
Tomato Powder
Whey
Paprika
Jalapeno Peppers
Malic Acid
Sour Cream
- Cultured Cream
- Skim Milk
Yeast Extract
Disodium Inosinate
Disodium Guanylate
Nutritional Benefits
| Nutrient | Quantity | Percentage |
| Total Fat | 10g | 12% |
| Saturated Fat | 1.5g | 7% |
| Trans Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 200mg | 9% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 15g | 6% |
| Dietary Fiber | <1g | 3% |
| Total Sugars | <1g | |
| Protein | 1g | |
| Vitamin D | 0 mcg | 0% |
| Calcium | 10mg | 0% |
| Iron | 0.7mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 40mg | 0% |
Cheetos Bolitas Cheese Flavored Snacks
Ingredients
Enriched Corn Meal
- Corn Meal
- Ferrous Sulfate
- Niacin
- Thiamin Mononitrate
- Riboflavin
- Folic Acid
Vegetable Oil
- Corn Oil
- Canola Oil
- Sunflower Oil
Whey
Cheddar Cheese
- Pasteurized Milk
- Cheese Cultures
- Salt
- Enzymes
Corn Syrup Solids
Buttermilk
Maltodextrin (Made From Corn)
Salt
Spices
Whole Milk
Monosodium Glutamate
Lactic Acid
Citric Acid
Natural and Artificial Flavors
Disodium Inosinate
Disodium Guanylate
Onion Powder
Malic Acid
Artificial Color
- Yellow 5 Lake
- Red 40 Lake
- Yellow 6 Lake
- Yellow 6
- Blue 1 Lake
Garlic Powder
Nutritional Benefits
| Nutrient | Quantity | Percentage |
| Total Fat | 12g | 15% |
| Saturated Fat | 2g | 9% |
| Trans Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 160mg | 7% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 14g | 5% |
| Dietary Fiber | <1g | 2% |
| Total Sugars | <1g | |
| Protein | 2g | |
| Vitamin D | 0 mcg | 0% |
| Calcium | 20mg | 0% |
| Iron | 0.4mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 40mg | 0% |
Cheetos Mexican Street Corn Cheese Flavored Snacks
Ingredients
Enriched Corn Meal
- Corn Meal
- Ferrous Sulfate
- Niacin
- Thiamin Mononitrate
- Riboflavin
- Folic Acid
Vegetable Oil
- Corn Oil
- Canola Oil
- Sunflower Oil
Maltodextrin (Made From Corn)
Salt
Natural Flavors
Whey
Spices
Monosodium Glutamate
Garlic Powder
Onion Powder
Sour Cream
- Cultured Cream
- Skim Milk
Cream
Parmesan Cheese
- Enzymes
- Milk
- Cheese Cultures
Romano Cheese
- Pasteurized Cow’s Milk
Yeast Extract
Artificial Color (Yellow 5 Lake)
Sugar
Cheddar Cheese
Butter
Swiss Cheese
Turmeric Extract
Nutritional Benefits
| Nutrient | Quantity | Percentage |
| Total Fat | 10g | 13% |
| Saturated Fat | 1.5g | 7% |
| Trans Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 200mg | 9% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 15g | 6% |
| Dietary Fiber | <1g | 3% |
| Total Sugars | <1g | |
| Protein | 2g | |
| Vitamin D | 0 mcg | 0% |
| Calcium | 10mg | 0% |
| Iron | 0.5mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 40mg | 0% |
Cheetos Crunchy Buffalo Flavored Snacks
Ingredients
Enriched Corn Meal
- Corn Meal
- Ferrous Sulfate
- Niacin
- Thiamin Mononitrate
- Riboflavin
- Folic Acid
Vegetable Oil
- Corn Oil
- Canola Oil
- Sunflower Oil
Maltodextrin (Made From Corn)
Garlic Powder
Hot Sauce
- Age Cayenne Red Pepper
- Vinegar
- Salt
- Garlic
Potassium Salt
Whey
Salt
Spices
Sour Cream
- Cream
- Skim Milk
- Cultures
Cheddar Cheese
- Milk
- Cheese Cultures
- Salt
- Enzymes
Natural Flavors
Sugar
Monosodium Glutamate
Chilean Salt
Onion Powder
Buttermilk
Yeast Extract
Sodium Diacetate
Cream Cheese
- Milk and Cream
- Xanthan Gum
- Carob Beam Gum
Medium Chain Triglycerides
Malic Acid
Artificial Color (Red 40 Lake)
Fermented Pea Protein
- Pea Protein
- Rice Powder
Disodium Guanylate
Disodium Inosinate
Nutritional Benefits
The Crunchy Buffalo flavor weighs 28g and it has 21 pieces in the sachet. In total you have 150 calories, 1.5g saturated fat, 150 mg sodium and less than 1g sugar.
| Nutrient | Quantity | Percentage |
| Total Fat | 10g | 13% |
| Saturated Fat | 1.5g | 7% |
| Trans Fat | 0g | 0% |
| Cholesterol | 0mg | 0% |
| Sodium | 200mg | 9% |
| Total Carbohydrate | 15g | 6% |
| Dietary Fiber | <1g | 3% |
| Total Sugars | <1g | |
| Protein | 2g | |
| Vitamin D | 0 mcg | 0% |
| Calcium | 10mg | 0% |
| Iron | 0.5mg | 2% |
| Potassium | 40mg | 0% |
When to take Cheetos
Anytime you think of having a snack, then having any of the Cheetos varieties as a treat wouldn’t be a bad idea. Whether watching your favorite movie, driving, or relaxing in a park, you can have your favorite Cheetos and have fun.
-

 Drinks3 weeks ago
Drinks3 weeks agoCody’s Vody energy drink contains up to 18% alcohol
-

 Drugs3 weeks ago
Drugs3 weeks agoAlmased Ingredients And Honest Review
-

 Drugs3 weeks ago
Drugs3 weeks agoOmega XL Ingredients and Honest Review
-

 Food3 weeks ago
Food3 weeks agoCheetos Snacks Ingredients and Honest Review
-

 Food3 weeks ago
Food3 weeks agoYoohoo Drink Ingredients and Honest Review
-

 Food3 weeks ago
Food3 weeks agoSour Patch Kids Ingredients and Honest Review
-

 Drinks3 weeks ago
Drinks3 weeks agoBullet Vodka Mixed Drink, 18% Alcohol, Ingredients and Price
-

 Drugs3 weeks ago
Drugs3 weeks agoPooph Ingredients and Honest Review